
Run Chart
-
A graphical tool that
displays data points in run
order
-
It is used to monitor process
performance (variation)
over time
– helps us
understand if we are
meeting customer
requirements on a regularly
-
Run chart helps us to
analyze the trends &
patterns over time (process
behavior)
-
It also helps us to identify
the drivers of performance
-
It’s useful for baselining our
process performance
-
It shows process
improvement
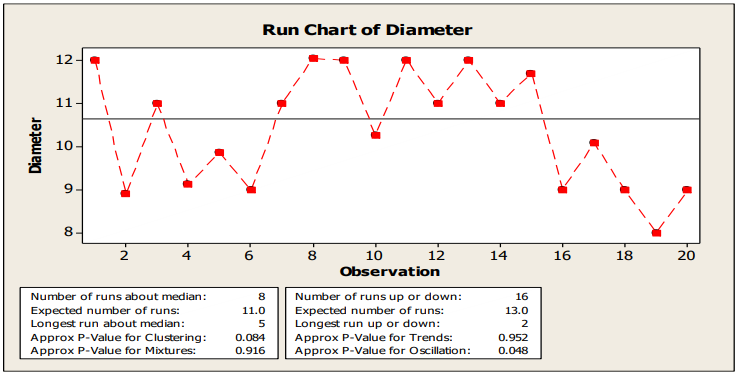
-
A Run is a series of points in a row on one side of the
median.
-
To determine the number of runs above and below the
median, count the number of times the data line crosses the
median and add one. Statistically, significant change is
signaled by too few or too many runs, again calculated using
statistical probability.
-
Number of runs about median
- The number of runs about the median is the total number of
runs above the median and the total number of runs below
the median.
- A run about the median is one or more consecutive points
on the same side of the center line. A run ends when the line
that connects the points crosses the center line. A new run
begins with the next plotted point
-
Number of runs up or down
- A run-up is an upward run of consecutive points that
exclusively increases. A rundown is a downward run of
consecutive points that exclusively decreases. A run ends
when the direction (either up or down) changes. For
example, when the preceding value is smaller, a run-up
begins and continues until the proceeding value is larger
than the next point, then a rundown begins.
-
Expected number of runs up or down
- The expected number of runs up or down is the number of
runs you would expect to have in your data if the data are
randomly distributed.

